| Content: | 300 Units (on sucrose) |
| Shipping Temperature: | Ambient |
| Storage Temperature: | Below -10oC |
| Formulation: | Supplied as a lyophilised powder |
| Physical Form: | Powder |
| Stability: | > 1 year under recommended storage conditions |
| Enzyme Activity: | Sucrase/Invertase |
| EC Number: | 3.2.1.20 |
| CAZy Family: | GH13 |
| CAS Number: | 9001-42-7 |
| Synonyms: | alpha-glucosidase; alpha-D-glucoside glucohydrolase |
| Source: | Yeast |
| Molecular Weight: | 62,000 |
| Expression: | Purified from Yeast |
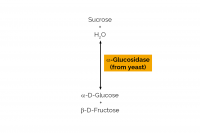
| Specificity: | Hydrolysis of terminal, non-reducing (1,4)-linked α-D-glucose residues with release of D-glucose. |
| Specific Activity: | ~ 20 U/mg (30oC, pH 6.8 on sucrose) |
| Unit Definition: | One Unit of sucrase activity is defined as the amount of enzyme required to release one µmole of glucose per minute from sucrose (10 mM) in sodium maleate buffer (100 mM), pH 6.8 at 30oC. |
| Temperature Optima: | 30oC |
| pH Optima: | 6.8 |
| Application examples: | Applications for the removal of sucrose in various analytical procedures in the cereals, food and feeds, fermentation and beverage industries. |
| Method recognition: | AOAC Method 2016.06 and GB Standard 5009.255-2016 |
High purity Sucrase (from yeast) for use in research, biochemical enzyme assays and analytical testing applications. Sucrase (E-SUCR) and Fructanase (E-FRMXLQ or E-FRMXPD) are used in the measurement of fructan in foods according to Chinese GB Standard 5009.255-2016 and in the AOAC method 2016.06.
For more products, see Carbohydrate Active enZYmes list.
Validation of Methods


Exploring the Inhibitory Potential of Sodium Alginate Against Digestive Enzymes Linked to Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes.
Daub, C. D., Michaels, A. L., Mabate, B., Mkabayi, L., Edkins, A. L. & Pletschke, B. I. (2025). Molecules, 30(5), 1155.
Obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) are major health concerns worldwide, often managed with treatments that have significant limitations and side effects. This study examines the potential of sodium alginates, extracted from Ecklonia radiata and Sargassum elegans, to inhibit digestive enzymes involved in managing these conditions. We chemically characterized the sodium alginates and confirmed their structural integrity using FTIR, NMR, and TGA. The focus was on evaluating their ability to inhibit key digestive enzymes relevant to T2DM (α-amylase, α-glucosidase, sucrase, maltase) and obesity (pancreatic lipase). Enzyme inhibition assays revealed that these sodium alginates moderately inhibit α-glucosidase, maltase, and lipase by up to 43%, while showing limited effects on sucrase and α-amylase. In addition, the sodium alginates did not affect glucose uptake in human colorectal cells (HCT116), indicating they do not impact cellular glucose absorption. In summary, while the observed enzyme inhibition was moderate, the targeted inhibition of α-glucosidase, maltase, and lipase suggests that sodium alginates could be beneficial for managing postprandial hyperglycemia and lipid absorption in the context of T2DM and obesity.
Hide AbstractThe molecular basis of the effect of temperature on enzyme activity.
Daniel, R. M., Peterson, M. E., Danson, M. J., Price, N. C., Kelly, S. M., Monk, C R., Weinberg, C S., Oudshoorn, M. L. & Lee, C. K. (2010). Biochem. J, 425, 353-360.
Experimental data show that the effect of temperature on enzymes cannot be adequately explained in terms of a two-state model based on increases in activity and denaturation. The Equilibrium Model provides a quantitative explanation of enzyme thermal behaviour under reaction conditions by introducing an inactive (but not denatured) intermediate in rapid equilibrium with the active form. The temperature midpoint (Teq) of the rapid equilibration between the two forms is related to the growth temperature of the organism, and the enthalpy of the equilibrium (ΔHeq) to its ability to function over various temperature ranges. In the present study, we show that the difference between the active and inactive forms is at the enzyme active site. The results reveal an apparently universal mechanism, independent of enzyme reaction or structure, based at or near the active site, by which enzymes lose activity as temperature rises, as opposed to denaturation which is global. Results show that activity losses below Teq) may lead to significant errors in the determination of ΔG*cat made on the basis of the two-state (‘Classical’) model, and the measured kcat will then not be a true indication of an enzyme's catalytic power. Overall, the results provide a molecular rationale for observations that the active site tends to be more flexible than the enzyme as a whole, and that activity losses precede denaturation, and provide a general explanation in molecular terms for the effect of temperature on enzyme activity.
Hide Abstract