50 assays (manual) / 500 assays (microplate) / 500 assays (auto-analyser)
| Content: | 50 assays (manual) / 500 assays (microplate) / 500 assays (auto-analyser) |
| Shipping Temperature: | Ambient |
| Storage Temperature: |
Short term stability: 2-8oC, Long term stability: See individual component labels |
| Stability: | > 2 years under recommended storage conditions |
| Analyte: | N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine, D-Glucosamine, D-Glucosamine sulphate |
| Assay Format: | Spectrophotometer, Microplate, Auto-analyser |
| Detection Method: | Absorbance |
| Wavelength (nm): | 340 |
| Signal Response: | Increase |
| Linear Range: | 4 to 80 µg of glucosamine per assay |
| Limit of Detection: | 1.33 mg/L |
| Reaction Time (min): | ~ 8 min |
| Application examples: | Food supplements, food products and beverages. |
| Method recognition: | Novel method |
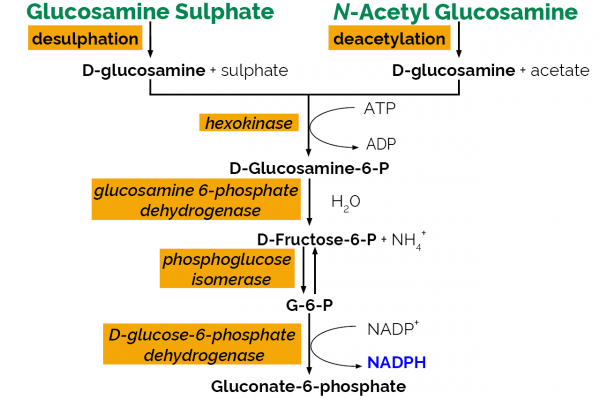
The D-Glucosamine test kit is a high purity reagent for the measurement and analysis of D-glucosamine in neutraceutical/food products. This kit can also be used to measure N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine and D-Glucosamine sulphate.
Note for Content: The number of manual tests per kit can be doubled if all volumes are halved. This can be readily accommodated using the MegaQuantTM Wave Spectrophotometer (D-MQWAVE).
See our complete list of monosaccharide and disaccharide assay kits.

- Novel product with simple format
- All reagents stable for > 2 years after preparation
- All enzymes supplied as stable suspensions
- Very rapid reaction
- Mega-Calc™ software tool is available from our website for hassle-free raw data processing
- Standard included
- Suitable for manual, microplate and auto-analyser formats
Role of putative APSES family transcription factor Swi6 in cell wall synthesis regulation in the agaricomycete Pleurotus ostreatus.
Kojima, H., Izumi, T., Kawauchi, M., Otsuka, Y., Tsuji, K., Yoshimi, A., Tanaka, C., Yano, S., Nakazawa, T. & Honda, Y. (2025). Fungal Biology, 129(1), 101526.
Clade A APSES family transcription factor Swi6 functions alongside Mbp1 to form the MBF (MluI cell cycle box-binding factor) complex in ascomycetes. In the agaricomycete Pleurotus ostreatus, Mbp1 plays a crucial role in regulating β-glucan and chitin synthesis; however, the role of Swi6 has not been explored in this fungus. In this study, its involvement in cell wall synthesis regulation was analysed using swi6 disruption strains in P. ostreatus. The Δswi6 strains exhibited reduced growth rates and shorter aerial hyphae formation in both agar and liquid media, suggesting an essential role of Swi6 in normal vegetative growth. Furthermore, swi6 disruption affected cell wall thickness distribution, the expression of specific chitin synthase genes, the relative percentage of chitin, and sensitivity to calcofluor white, suggesting that Swi6 is required for normal chitin synthesis regulation in P. ostreatus. In contrast, no significant differences were observed between the wild-type and Δswi6 strains in the relative percentage of α- and β-glucan and the expression of α- and β-glucan synthase genes, suggesting its unimportant role in α- and β-glucan synthesis regulation. In conclusion, Swi6 is necessary for normal mycelial growth and chitin synthesis regulation in P. ostreatus. To the best of our knowledge, this study is the first report on the functional differences and overlaps between Mbp1 and Swi6 in the regulation of cell wall synthesis in agaricomycetes.
Hide AbstractDysfunction of astrocytic glycophagy exacerbates reperfusion injury in ischemic stroke.
Guo, H., Li, Y., Wang, S., Yang, Y., Xu, T., Zhao, J., Wang, J., Zuo, W., Wang, P., Zhao, G.,Wang., H, Hou, W., Dong,H. & Cai, Y. (2024). Redox Biology, 103234.
Glycophagy has evolved from an alternative glycogen degradation pathway into a multifaceted pivot to regulate cellular metabolic hemostasis in peripheral tissues. However, the pattern of glycophagy in the brain and its potential therapeutic impact on ischemic stroke remain unknown. Here, we observed that the dysfunction of astrocytic glycophagy was caused by the downregulation of the GABA type A receptor-associated protein like 1 (GABARAPL1) during reperfusion in ischemic stroke patients and mice. PI3K-Akt pathway activation is involved in driving GABARAPL1 downregulation during cerebral reperfusion. Moreover, glycophagy dysfunction-induced glucosamine deficiency suppresses the nuclear translocation of specificity protein 1 and TATA binding protein, the transcription factors for GABARAPL1, by decreasing their O-GlcNAcylation levels, and accordingly feedback inhibits GABARAPL1 in astrocytes during reperfusion. Restoring astrocytic glycophagy by overexpressing GABARAPL1 decreases DNA damage and oxidative injury in astrocytes and improves the survival of surrounding neurons during reperfusion. In addition, a hypocaloric diet in the acute phase after cerebral reperfusion can enhance astrocytic glycophagic flux and accelerate neurological recovery. In summary, glycophagy in the brain links autophagy, metabolism, and epigenetics together, and glycophagy dysfunction exacerbates reperfusion injury after ischemic stroke.
Hide AbstractCritical evaluation of a putative glucosamine excretion by Aspergillus niger CBS120. 49 and Penicillium ochrochloron CBS123. 824 under citric acid producing conditions.
Artmann, D. J., Amrain, W., Murauer, A., Ganzera, M., Vrabl, P., Schinagl, C. W. & Burgstaller, W. (2019). Scientific Reports, 9(1), 1-9.
As one of the most frequently occurring monomers in the biosphere, glucosamine is a valuable metabolite for several applications. Although microbial glucosamine production is still in its infancy, it offers the possibility to circumvent problems associated with traditional production by hydrolysis. Of particular interest is a study with Aspergillus niger, which reports for the first time high glucosamine excretion in the early phase of citric acid production. These results have relevance for both the commercial glucosamine production and deeper insight into the regulation of organic acid excretion in fungi. To investigate glucosamine excretion, we performed bioreactor batch cultivations with Penicillium ochrochloron CBS123.824 and A. niger CBS120.49 using cultivation conditions which are known to trigger the production of citric acid. Glucosamine detection in culture filtrates was achieved by two photometric methods, High performance liquid chromatography with evaporative light scattering detection (HPLC-ELSD) and HPLC with mass spectrometry detection (HPLC-MS). Surprisingly, we detected no glucosamine at all. Based on a critical review of published data for A. niger, we conclude that the reported high levels of excreted glucosamine might be an experimental artifact. However, growth experiments with glucosamine as a combined or single source for carbon or nitrogen showed that both organisms are in principle able to transport glucosamine across their plasma membrane, which is a prerequisite for the excretion of glucosamine.
Hide AbstractDeficiency of AtGFAT1 activity impairs growth, pollen germination and tolerance to tunicamycin in Arabidopsis.
Vu, K. V., Jeong, C. Y., Nguyen, T. T., Dinh, T. T. H., Lee, H., & Hong, S. W. (2019). Journal of Experimental Botany, 70(6), 1775-1787.
The hexosamine biosynthetic pathway (HBP) plays essential roles in growth and development in plants. However, insight into the biological function of glutamine:fructose-6-phosphate amidotransferase 1 (GFAT1), mediating the first regulatory step of the HBP, remains unclear in plants. Here, we report the molecular characterization of Arabidopsis AtGFAT1 gene. AtGFAT1 was highly expressed in mature pollen grains, but its expression was not detectable in the rest of the organs. Pollen grains bearing the gfat1-2 knockout allele displayed defects in a polar deposition of pectin and callose in the pollen cell wall, leading to no genetic transmission of the gfat1-2 allele through the male gametophyte. AtGFAT1 overexpression increased glucosamine (GlcN) content and enhanced resistance to tunicamycin (Tm) treatment, while RNAi-mediated suppression reduced GlcN content and resistance to Tm treatment. However, the decrease in Tm resistance by RNAi suppression of AtGFAT1 was recovered by a GlcN supplement. The exogenous GlcN supplement also rescued gfat1-2/gaft1-2 mutant plants, which were otherwise not viable. The gfat1-2/gfat1-2 plants stopped growing at the germination stage on GlcN-free medium, but GlcN supplement allowed wild-type growth of gfat1-2/gfat1-2 plants. In addition, reactive oxygen species production, cell death and a decrease in protein N-glycosylation were observed in gfat1-2/gaft1-2 mutant plants grown on GlcN-free medium, whereas these aberrant defects were not detectable on GlcN-sufficient medium. Taken together, these results show that the reduction of protein N-glycosylation was at least partially responsible for many aberrant phenotypes in growth and development as well as the response to Tm treatment caused by AtGFAT1 deficiency in Arabidopsis.
Hide AbstractBoguś, M. I., Włóka, E., Wrońska, A., Kaczmarek, A., Kazek, M., Zalewska, K., Ligeza-Zuber, M. & Gołębiowski, M. (2016). Medical and Veterinary Entomology, 31(1), 23-35.
Entomopathogenic fungi infect insects via penetration through the cuticle, which varies remarkably in chemical composition across species and life stages. Fungal infection involves the production of enzymes that hydrolyse cuticular proteins, chitin and lipids. Host specificity is associated with fungus–cuticle interactions related to substrate utilization and resistance to host-specific inhibitors. The soil fungus Conidiobolus coronatus (Constantin) (Entomophthorales: Ancylistaceae) shows virulence against susceptible species. The larvae and pupae of Calliphora vicina (Robineau-Desvoidy) (Diptera: Calliphoridae), Calliphora vomitoria (Linnaeus), Lucilia sericata (Meigen) (Diptera: Calliphoridae) and Musca domestica (Linnaeus) (Diptera: Muscidae) are resistant, but adults exposed to C. coronatus quickly perish. Fungus was cultivated for 3 weeks in a minimal medium. Cell-free filtrate, for which activity of elastase, N-acetylglucosaminidase, chitobiosidase and lipase was determined, was used for in vitro hydrolysis of the cuticle from larvae, puparia and adults. Amounts of amino acids, N-glucosamine and fatty acids released were measured after 8 h of incubation. The effectiveness of fungal enzymes was correlated with concentrations of compounds detected in the cuticles of tested insects. Positive correlations suggest compounds used by the fungus as nutrients, whereas negative correlations may indicate compounds responsible for insect resistance. Adult deaths result from the ingestion of conidia or fungal excretions.
Hide AbstractExtraction of Glycosaminoglycans Containing Glucosamine and Chondroitin Sulfate from Chicken Claw Cartilage.
Widyaningsih, T. D., Rukmi, W. D., Sofia, E., Wijayanti, S. D., Wijayanti, N., Ersalia, R., Rochmawati, N. & Nangin, D. (2016). Research Journal of Life Science, 3(3), 181-189.
Chicken cartilage (claw) is a waste of chicken cuts which are widely available in Indonesia. Cartilage part of chicken claw becomes a potential source of chondroitin sulfate (CS) and glucosamine (GS). This study aims to determine the most optimal extraction methods of CS and GS from cartilage of chicken claw. Various types of extraction methods used in this study are taken from the extraction by using boiling water (2 and 2.5 hours), acetic acid (7 and 17 hours), as well as proteolysis by papain (24 and 48 hours). Parameters observed include chemical characteristics of powdered cartilage of chicken claw as well as CS and GS levels in powdered cartilage of chicken claw extract. The results of this research show that the levels of CS and GS of chicken claw cartilage powder were 2.17% and 13%. Meanwhile, the highest GS level was obtained from the extraction with water treatment for 2.5 hours which was 8.1%. The treatment and duration of extraction will significantly affect the number of GS which was produced. The highest content of CS was obtained from the extraction with the enzyme treatment for 48 hours which was 2.47%. The best treatment is the extraction with water treatment for 2.5 hours which were the extracts with GS levels of 8.1% and 2.03% CS was selected through the analysis of multiple attribute.
Hide AbstractTsai, J. H., Schulte, M., O'Neill, K., Chi, M. M. Y., Frolova, A. I. & Moley, K. H. (2013). Biology of Reproduction, 89(1), 16, 1-10.
Embryo implantation in the uterus depends on decidualization of the endometrial stromal cells (ESCs), and glucose utilization via the pentose phosphate pathway is critical in this process. We hypothesized that the amino sugar glucosamine may block the pentose phosphate pathway via inhibition of the rate-limiting enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in ESCs and therefore impair decidualization and embryo implantation, thus preventing pregnancy. Both human primary and immortalized ESCs were decidualized in vitro in the presence of 0, 2.5, or 5 mM glucosamine for 9 days. Viability assays demonstrated that glucosamine was well tolerated by human ESCs. Exposure of human ESCs to glucosamine resulted in significant decreases in the activity and expression of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and in the mRNA expression of the decidual markers prolactin, somatostatin, interleukin-15, and left-right determination factor 2. In mouse ESCs, expression of the decidual marker Prp decreased upon addition of glucosamine. In comparison with control mice, glucosamine-treated mice showed weak artificial deciduoma formation along the stimulated uterine horn. In a complementary in vivo experiment, a 60-day-release glucosamine (15, 150, or 1500 µg) or placebo pellet was implanted in a single uterine horn of mice. Mice with a glucosamine pellet delivered fewer live pups per litter than those with a control pellet, and pup number returned to normal after the end of the pellet-active period. In conclusion, glucosamine is a nonhormonal inhibitor of decidualization of both human and mouse ESCs and of pregnancy in mice. Our data indicate the potential for development of glucosamine as a novel, reversible, nonhormonal contraceptive.
Hide Abstract